Finland is located in the north part of the globe and positioned between Sweden and Russia. From the north, Finland ...
Finland gained the independence on the 6th of December 1917. Before this, Finland was under the Russian rule between ...
The forest industry is still a very important source of livelihood in Finland and used to be one of the main sources in the ...
Similar rights and responsibilities apply to the immigrants and the native Finns. Immigrants have the right to practice their ...
Women and men are considered equal in Finland. The members of the Parliament and the Government are almost ...
Hand shaking and nodding are usual ways of greeting in Finland. Close friends or family members can greet each other by ...
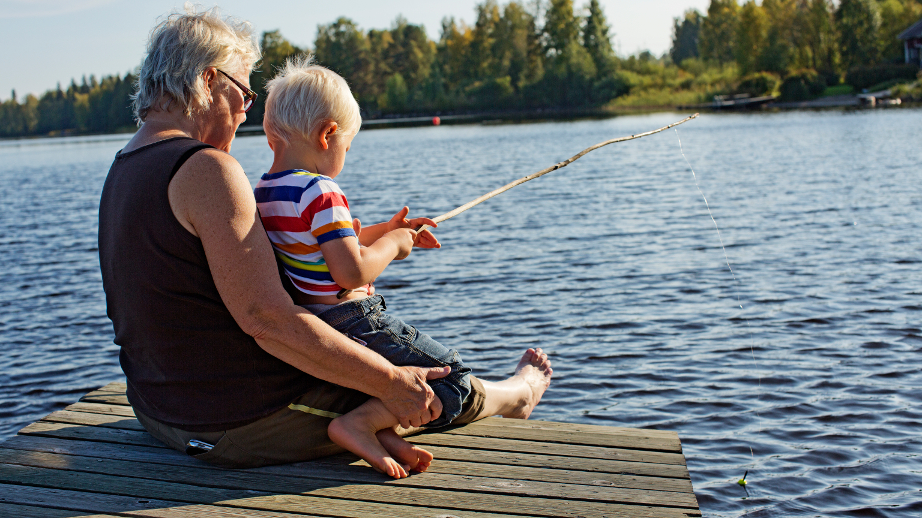
Finland has four distinct seasons: spring, summer, autumn and winter. The temperature changes a lot between these ...
Finland is located in the north part of the globe and positioned between Sweden and Russia. From the north, Finland shares a border with Norway. On the south side of Finland is Estonia. The official languages in Finland are Finnish and Swedish. The population of Finland is approximately 5.5 million people. There are about 200 000 foreign language speakers in the country.
The freedom of religion is reinforced by law in Finland. The main religion is Christianity. The largest church is the Evangelical Lutheran church to which approximately 80 percent of the population belongs, and the next largest is the Orthodox church with 1 percent of the population. There are tens of thousands of Muslims in Finland. Other religious groups include the Jehovas witnesses, Finland's Free Church, the Catholic Church and the Adventist Church of Finland.
Finland gained the independence on the 6th of December 1917. Before this, Finland was under the Russian rule between the years of 1809–1917, although Finland had some autonomy over its decisions. Before that, Finland belonged to Sweden for 600 years of period.
Finland is a democratic republic. The head of state is the President, who is chosen through elections every six years. The same person can be a president up to two consequent tenures.
In Finland, all men and women over the age of 18 have the right to vote. Women gained the right to vote in the year 1906, as one of the first countries in the world. In Finland there is a multiparty system and there are at the moment eight parties.
The Finnish parliament regulates the laws in Finland and decides the state budget. There are 200 members of the Parliament. The members of the Parliament are chosen for four years at a time. The government prepares and executes the decisions of the Parliament. The government is made up of the Prime Minister and all other ministers.
Finland divides into municipalities which are autonomic. Municipalities have the right to collect taxation from its residents and decide over its budget. Municipalities have the duty to provide services to its residents, such as health care, social services and basic education.

The forest industry is still a very important source of livelihood in Finland and used to be one of the main sources in the history. A large portion of the surface area of Finland is forests. Forests have been called as the Finnish green gold. Agriculture is still an important source of livelihood, but since it has become mechanized, it only provides work to a small number of Finns.
Finland became industrialized in the 1950’s. The development of industrialization allowed Finland to become a part of the economic development of Europe. Some important industrial trades include ship building and forest industry. During the last decades technology has risen to be an important industrial field, and in the last years, the game industry has become an important sector in industry. Significant employers in Finland are the technological and service related fields.
Similar rights and responsibilities apply to the immigrants and the native Finns. Immigrants have the right to practice their own religion and to celebrate the festive days of their own calendars and religions. Immigrants have established their own religious communities and meeting spaces all over Finland. The Finns' attitude towards immigrants is usually friendly. There is some resistance but discrimination is forbidden by law in Finland.
Women and men are considered equal in Finland. The members of the Parliament and the Government are almost 50 percent female. Most women go to work outside of the home and men take part in household duties and take care of the children. Violence against women is a crime as well as all other violence towards other people at home or outside of the home.
The position of the children is good in Finland. Wellbeing of the child is taken care of even before the birth in maternity clinics. Children cannot be hit nor pulled by the hair. Finland has a good kindergarten system, and all children aged 7–16 go to primary and secondary education.


Hand shaking and nodding are usual ways of greeting in Finland. Close friends or family members can greet each other by hugging. In big cities people normally greet only those they know. When greeting, people look each others in the eyes.
The Finns usually start a conversation with a stranger very carefully. Because of this the Finnish people may come across as shy and rude. Usually Finns do not ask for many turns to speak in public discussions and they usually get to the point quickly.
Equality and justice are important values to the Finns. Also Finns appreciate honesty and keeping promises. Working and being diligent is appreciated a lot. Punctuality and following on agreed times is important.
Many Finns use a lot of alcohol especially on the weekends and special festive holidays, which might confuse immigrants. Excessive use of alcohol can cause diseases and also conflicts in the families.

Finland has four distinct seasons: spring, summer, autumn and winter. The temperature changes a lot between these seasons. The weather can be very different in different parts of the country. Northern Finland is much colder than Southern Finland.
The spring seasons begins in March and lasts until May. During the spring the snow and ice melt away. The nature wakes up. The leaves grow on trees and plants start to grow. People start to move more outside and enjoy the increased sunlight.
The months of summer are June, July and August. The warmest month is July. During the summer it is light also in the evening and at night. The sun sets late at night and rises early. During the summer the Finnish people spend a lot of time outside together. Social life is livelier and people are more open. Summer is also a holiday season.
Autumn begins in September and ends in November. During the fall the weather gets colder and it rains a lot. The leaves fall off the trees. The amount of daylights lessens and the weather gets colder and people must be prepared for it with warm clothing. During the fall people focus on doing work, studying and hobbies.
December, January and February are cold months in Finland. During the winter it snows a lot and the ground is covered in snow. The coldest month of the year is February. In order to survive the cold weather you must wear warm clothes outside and learn to dress in layers. Because of the freezing weather conditions people prefer to stay indoors, but a normal life continues.
